16.1 Weather and Water in the Atmosphere
Lesson Objectives
- Explain what causes weather.
- Describe humidity and its role in weather.
- Explain how clouds are classified.
- Identify types of precipitation and how they form.
Vocabulary
- cirrus cloud
- cumulus cloud
- dew point
- fog
- freezing rain
- hail
- heat index
- humidity
- relative humidity
- sleet
- stratus cloud
- weather
Introduction
If someone in a distant place were to ask what your weather is like today, what would you say? How would you describe the weather right now where you are? Is it warm or cold? Sunny or cloudy? Calm or windy? Clear or rainy? What features of weather are important to mention?
What Is Weather?
What do temperature, clouds, winds, and rain have in common? They are all part of weather. Weather refers to the conditions of the atmosphere at a given time and place.
What Causes Weather?
Weather occurs because of unequal heating of the atmosphere. The source of heat is the Sun. The general principles behind weather can be stated simply:
- The Sun heats Earth’s surface more in some places than others.
- Where it is warm, heat from the Sun warms the air close to the surface. If there is water at the surface, it may cause some of the water to evaporate.
- Warm air is less dense, so it rises. When this happens, more dense air flows in to take its place. The flowing surface air is wind.
- The rising air cools as it goes higher in the atmosphere. If it is moist, the water vapor may condense. Clouds may form, and precipitation may fall.
Weather and the Water Cycle
The water cycle plays an important role in weather. When liquid water evaporates, it causes humidity. When water vapor condenses, it forms clouds and precipitation. Humidity, clouds, and precipitation are all important weather factors.
Humidity
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. High humidity increases the chances of clouds and precipitation.
Relative Humidity
Humidity usually refers to relative humidity. This is the percent of water vapor in the air relative to the total amount the air can hold. How much water vapor can the air hold? That depends on temperature. Warm air can hold more water vapor than cool air. You can see this in Figure below.
How much water vapor can the air hold when its temperature is 40° C?
Humidity and Heat
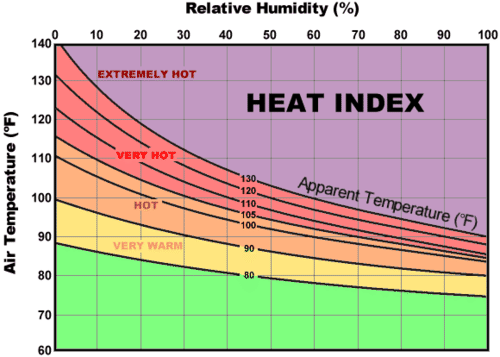
People often say, “it’s not the heat but the humidity.” Humidity can make a hot day feel even hotter. When sweat evaporates, it cools your body. But sweat can’t evaporate when the air already contains as much water vapor as it can hold. The heat index is a measure of what the temperature feels like because of the humidity. You can see the heat index in Figure below.
How hot does it feel when the air temperature is 90°F? It depends on the humidity.
Dew Point
You’ve probably noticed dew on the grass on a summer morning. Why does dew form? Remember that the land heats up and cools down fairly readily. So when night comes, the land cools. Air that was warm and humid in the daytime also cools over night. As the air cools, it can hold less water vapor. Some of the water vapor condenses on the cool surfaces, such as blades of grass. The temperature at which water vapor condenses is called the dew point. If this temperature is below freezing, ice crystals of frost form instead of dew. As you can see in Figure above, the dew point occurs at 100 percent relative humidity. Can you explain why?
Clouds
Clouds form when air in the atmosphere reaches the dew point. Clouds may form anywhere in the troposphere. Clouds that form on the ground are called fog.
How Clouds Form
Clouds form when water vapor condenses around particles in the air. The particles are specks of matter, such as dust or smoke. Billions of these tiny water droplets come together to make up a cloud. If the air is very cold, ice crystals form instead of liquid water.
Classification of Clouds
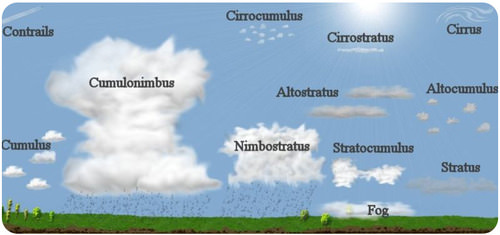
Clouds are classified on the basis of where and how they form. Three main types of clouds are cirrus, stratus, and cumulus. Figure below shows these and other types of clouds.
- Cirrus clouds form high in the troposphere. Because it is so cold they are made of ice crystals. They are thin and wispy. Cirrus clouds don’t usually produce precipitation, but they may be a sign that wet weather is coming.
- Stratus clouds occur low in the troposphere. They form in layers that spread horizontally and may cover the entire sky like a thick blanket. Stratus clouds that produce precipitation are called nimbostratus. The prefix nimbo- means “rain.”
- Cumulus clouds are white and puffy. Convection currents make them grow upward and they may grow very tall. When they produce rain, they are called cumulonimbus.
Find the cirrus, cirrostratus, and cirrocumulus clouds in the figure. What do they have in common? They all form high in the troposphere. Clouds that form in the mid troposphere have the prefix “alto-”, as in altocumulus. Where do stratocumulus clouds form?
Clouds and Temperature
Clouds can affect the temperature on Earth’s surface. During the day, thick clouds block some of the Sun’s rays. This keeps the surface from heating up as much as it would on a clear day. At night, thick clouds prevent heat from radiating out into space. This keeps the surface warmer than it would be on a clear night.
Precipitation
Clouds are needed for precipitation. This may fall as liquid water, or it may fall as frozen water, such as snow.
Why Precipitation Falls
Millions of water molecules in a cloud must condense to make a single raindrop or snowflake. The drop or flake falls when it becomes too heavy for updrafts to keep it aloft. As a drop or flake falls, it may collect more water and get larger.
Types of Precipitation
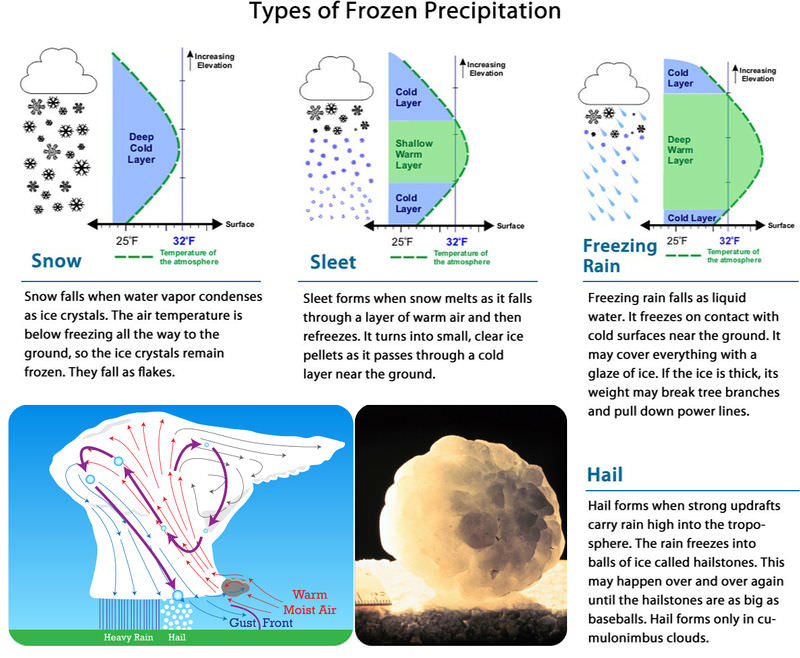
Why does it snow instead of rain? Air temperature determines which type of precipitation falls. Rain falls if the air temperature is above freezing (0° C or 32° F). Frozen precipitation falls if the air or ground is below freezing. Frozen precipitation may fall as snow, sleet, or freezing rain. You can see how the different types form in Figure below.
Frozen precipitation may fall as snow, sleet, or freezing rain.
Snow falls when water vapor condenses as ice crystals. The air temperature is below freezing all the way to the ground, so the ice crystals remain frozen. They fall as flakes. Sleet forms when snow melts as it falls through a layer of warm air and then refreezes. It turns into small, clear ice pellets as it passes through a cold layer near the ground. Freezing rain falls as liquid water. It freezes on contact with cold surfaces near the ground. It may cover everything with a glaze of ice. If the ice is thick, its weight may break tree branches and pull down power lines. Hail is another type of frozen precipitation. Hail forms in thunderstorms when strong updrafts carry rain high into the troposphere. The rain freezes into balls of ice called hailstones. This may happen over and over again until the hailstones are as big as baseballs. Hail forms only in cumulonimbus clouds.
Lesson Summary
- Weather refers to conditions of the atmosphere at a given time and place. It occurs because of unequal heating of the atmosphere. Humidity, clouds, and precipitation are important weather factors.
- Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Relative humidity is the percent of water vapor in the air relative to the total amount the air can hold. The total amount depends on temperature.
- Clouds form when water vapor condenses in the air around specs of matter. Clouds are classified on the basis of where and how they form. Types of clouds include cirrus, stratus, and cumulus clouds.
- Precipitation is water that falls from clouds. It may fall as liquid or frozen water. Types of frozen precipitation include snow, sleet, freezing rain, and hail.
Lesson Review Questions
Recall
1. What is weather?
2. List three weather factors.
3. What is humidity?
4. How do clouds form?
5. Identify sleet, freezing rain, and hail.
Apply Concepts
6. Classify the clouds pictured in Figure below.
Think Critically
7. Explain how dew point is related to air temperature and relative humidity.
8. You are lying in your sleeping bag on a cold morning. Your sleeping bag is wet with water. You know it didn't rain last night. What happened?
9. Infer why hail forms only in cumulonimbus clouds.
Points to Consider
A clear sky can quickly become covered with clouds. The clouds may bring a change in the weather.
- Why does a clear day turn cloudy?
- What causes weather to change?
- Log in or register to post comments
- Email this page