17.3 Climate Change
17.3 Climate Change
Lesson Objectives
- Outline how Earth’s climate has changed over time.
- Identify causes and effects of climate change.
- Describe El Niño and La Niña.
Vocabulary
- El Niño
- global warming
- ice age
- La Niña
Introduction
The weather changes all the time. It can change in a matter of minutes. Changes in climate occur more slowly, and the changes tend to be small. But even small changes in climate can make a big difference for Earth and its living things.
How Earth’s Climate Has Changed
Earth’s climate has changed many times through Earth's history. It’s been both hotter and colder than it is today.
The Big Picture
Over much of Earth’s past, the climate was warmer than it is today. Picture in your mind dinosaurs roaming the land. They're probably doing it in a pretty warm climate! But ice ages also occurred many times in the past. An ice age is a period when temperatures are cooler than normal. This causes glaciers to spread to lower latitudes. Scientists think that ice ages occurred at least six times over the last billion years alone. How do scientists learn about Earth’s past climates?
Pleistocene Ice Age
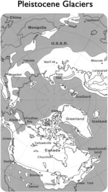
The last major ice age took place in the Pleistocene. This epoch lasted from 2 million to 14,000 years ago. Earth’s temperature was only 5° C (9° F) cooler than it is today. But glaciers covered much of the Northern Hemisphere. In Figure below, you can see how far south they went. Clearly, a small change in temperature can have a big impact on the planet. Humans lived during this ice age.
Pleistocene glaciers covered an enormous land area. Chicago is just one city that couldn't have existed during the Pleistocene.
Earth’s Recent Temperature
Since the Pleistocene, Earth’s temperature has risen. Figure below shows how it changed over just the last 1500 years. There were minor ups and downs. But each time, the anomaly (the difference from average temperature) was less than 1° C (1.8° F).
Earth’s temperature. Different sets of data all show an increase in temperature since about 1880 (the Industrial Revolution).
Since the mid 1800s, Earth has warmed up quickly. Look at Figure below. The 14 hottest years on record have all occurred since 1900. Eight of them have occurred since 1998! This is what is usually meant by global warming.
Earth’s temperature (1850–2007). Earth has really heated up over the last 150 years. Do you know why?
Explaining Long-Term Climate Change
Natural processes caused earlier climate changes. Human beings are the main cause of recent global warming.
Causes of Climate Change in Earth History
Several natural processes may affect Earth’s temperature. They range from sunspots to Earth’s wobble.
- Sunspots are storms on the Sun. When the number of sunspots is high, the Sun gives off more energy than usual. Still, there is little evidence for climate changing along with the sunspot cycle.
- Plate movements cause continents to drift closer to the poles or the equator. Ocean currents also shift when continents drift. All these changes can affect Earth’s temperature.
- Plate movements trigger volcanoes. A huge eruption could spew so much gas and ash into the air that little sunlight would reach the surface for months or years. This could lower Earth’s temperature.
- A large asteroid hitting Earth would throw a lot of dust into the air. This could block sunlight and cool the planet.
- Earth goes through regular changes in its position relative to the Sun. Its orbit changes slightly. Earth also wobbles on its axis of rotation. The planet also changes the tilt on its axis. These changes can affect Earth’s temperature.
Causes of Global Warming
Recent global warming is due mainly to human actions. Burning fossil fuels adds carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. It’s one of several that human activities add to the atmosphere. An increase in greenhouse gases leads to greater greenhouse effect. The result is increased global warming. Figure below shows the increase in carbon dioxide since 1960.
How much more carbon dioxide was in the air in 2005 than in 1960?
Effects of Global Warming
As Earth has gotten warmer, sea ice has melted. This has raised the level of water in the oceans. Figure below shows how much sea level has risen since 1880.
How much did sea level rise between 1880 and 2000?
Other effects of global warming include more extreme weather. Earth now has more severe storms, floods, heat waves, and droughts than it did just a few decades ago. Many living things cannot adjust to the changing climate. For example, coral reefs are dying out in all the world’s oceans.
How Will Climate Change in the Future?
Earth’s temperature will keep rising unless greenhouse gases are curbed. The temperature in 2100 may be as much as 5° C (9° F) higher than it was in 2000. Since the glacial periods of the Pleistocene, average temperature has risen about 4° C. That's just 4° C from abundant ice to the moderate climate we have today. How might a 5° C increase in temperature affect Earth in the future?
Warming will affect the entire globe by the end of this century. The map in Figure below shows the average temperature in the 2050s. This is compared with the average temperature in 1971 to 2000. In what place is the temperature increase the greatest? Where in the United States is the temperature increase the highest?
The Arctic will experience the greatest temperature changes.
As temperature rises, more sea ice will melt. Figure below shows how much less sea ice there may be in 2050 if temperatures keep going up. This would cause sea level to rise even higher. Some coastal cities could be under water. Millions of people would have to move inland. How might other living things be affected?
In the 2050s, there may be only half as much sea ice as there was in the 1950s.
Short-Term Climate Change
You’ve probably heard of El Niño and La Niña. These terms refer to certain short-term changes in climate. The changes are natural and occur in cycles. To understand the changes, you first need to know what happens in normal years. This is shown in Figure below.
This diagram represents the Pacific Ocean in a normal year. North and South America are the brown shapes on the right.
El Niño
During an El Niño, the western Pacific Ocean is warmer than usual. This causes the trade winds to change direction. The winds blow from west to east instead of east to west. This is shown in Figure below. The warm water travels east across the equator, too. Warm water piles up along the western coast of South America. This prevents upwelling. Why do you think this is true?
These changes in water temperature, winds, and currents affect climates worldwide. The changes usually last a year or two. Some places get more rain than normal. Other places get less. In many locations, the weather is more severe.
How do you think El Niño affects climate on the western coast of South America?
La Niña
La Niña generally follows El Niño. It occurs when the Pacific Ocean is cooler than normal. Figure below shows what happens. The trade winds are like they are in a normal year. They blow from east to west. But in a La Niña the winds are stronger than usual. More cool water builds up in the western Pacific. These changes can also affect climates worldwide.
How do you think La Niña affects climate on the western coast of South America?
Global Warming and Short-Term Climate Change
Some scientists think that global warming is affecting the cycle of El Niño and La Niña. These short-term changes seem to be cycling faster now than in the past. They are also more extreme.
Lesson Summary
- Earth’s climate has changed many times. Long warm periods were broken up by ice ages. Over the past 150 years, climate has warmed quickly.
- Climate change in Earth history was due to natural processes. Recent global warming is due mainly to human actions. The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the air. This creates greater greenhouse effect and global warming.
- El Niño and La Niña are short-term climate changes. They occur in cycles and influence weather all over the planet. They may be affected by global warming since El Niño is triggered by warmer ocean temperatures.
Lesson Review Questions
Recall
1. What is an ice age?
2. Describe the Pleistocene ice age.
3. Outline recent changes in Earth’s temperature.
4. What does global warming usually refer to?
5. Identify three natural causes of climate change.
6. List two effects of global warming.
Apply Concepts
7. Create a public service announcement about global warming. Explain how global warming is related to human actions and what people can do to reduce it. (Hint: How can people produce less carbon dioxide?)
Think Critically
8. Compare and contrast El Niño and La Niña.
9. Nearly all scientists are united in saying that human activities are causing much of the warming we see. Why do you think politicians are reluctant to believe them? Why is the public reluctant to believe them?
Points to Consider
A place’s climate determines what kinds of plants and animals can live there.
- Would you expect similar plants and animals to be found in the same type of climate all over the world?
- Besides climate, what factors might influence which plants and animals are found in a place?
- Log in or register to post comments
- Email this page