13.1 Water on Earth
13.1 Water on Earth
Lesson Objectives
- Describe water and where it occurs on Earth.
- Give an overview of the water cycle.
Vocabulary
- condensation
- evaporation
- freshwater
- infiltration
- precipitation
- runoff
- transpiration
- water
- water cycle
Introduction
Water is all around you — in pipes, in puddles, even in people. Water covers more than 70 percent of Earth’s surface. That’s a good thing, because all life on Earth depends on water. In fact, without water, life as we know it could not exist. Water is a very special substance. Do you know why?
What Is Water?
Water is a simple chemical compound. Each molecule of water contains two hydrogen atoms (H2) and one oxygen atom (O). That’s why the chemical formula for water is H2O.
If water is so simple, why is it special? Water is one of the few substances that exists on Earth in all three states of matter. Water occurs as a gas, a liquid and a solid. You drink liquid water and use it to shower. You breathe gaseous water vapor in the air. You may go ice skating on a pond covered with solid water — ice — in the winter.
Where Is Earth’s Freshwater?
Earth is often called the “water planet.” Figure below shows why. If astronauts see Earth from space, this is how it looks. Notice how blue the planet appears. That’s because oceans cover much of Earth’s surface. Water is also found in the clouds that rise above the planet.
Take a look at this image. Do you think that Earth deserves the name “water planet”?
Most of Earth’s water is salt water in the oceans. As Figure below shows, only 3 percent of Earth’s water is fresh. Freshwater is water that contains little or no dissolved salt. Most freshwater is frozen in ice caps and glaciers. Glaciers cover the peaks of some tall mountains. For example, the Cascades Mountains in North America and the Alps Mountains in Europe are capped with ice. Ice caps cover vast areas of Antarctica and Greenland. Chunks of ice frequently break off ice caps. They form icebergs that float in the oceans.
What percentage of Earth’s surface freshwater is water vapor in the air?
Only a tiny fraction of Earth’s freshwater is in the liquid state. Most liquid freshwater is under the ground in layers of rock. Of freshwater on the surface, the majority occurs in lakes and soil. What percentage of freshwater on the surface is found in living things?
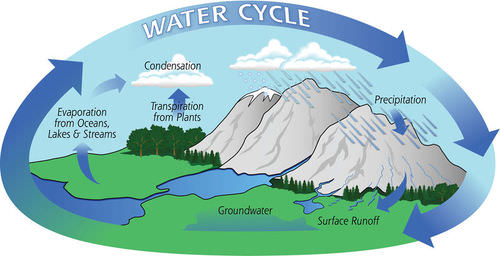
The Water Cycle
Did you ever wonder where the water in your glass came from or where it's been? The next time you take a drink of water, think about this. Each water molecule has probably been around for billions of years. That’s because Earth’s water is constantly recycled.
How Water Is Recycled
Water is recycled through the water cycle. The water cycle is the movement of water through the oceans, atmosphere, land, and living things. The water cycle is powered by energy from the Sun. Figure below diagrams the water cycle.
The water cycle has no beginning or end. Water just keeps moving along.
Processes in the Water Cycle
Water keeps changing state as it goes through the water cycle. This means that it can be a solid, liquid, or gas. How does water change state? How does it keep moving through the cycle? As Figure above shows, several processes are involved.
- Evaporation changes liquid water to water vapor. Energy from the Sun causes water to evaporate. Most evaporation is from the oceans because they cover so much area. The water vapor rises into the atmosphere.
- Transpiration is like evaporation because it changes liquid water to water vapor. In transpiration, plants release water vapor through their leaves. This water vapor rises into the atmosphere.
- Condensation changes water vapor to liquid water. As air rises higher into the atmosphere, it cools. Cool air can hold less water vapor than warm air. So some of the water vapor condenses into water droplets. Water droplets may form clouds.
- Precipitation is water that falls from clouds to Earth’s surface. Water droplets in clouds fall to Earth when they become too large to stay aloft. The water falls as rain if the air is warm. If the air is cold, the water may freeze and fall as snow, sleet, or hail. Most precipitation falls into the oceans. Some falls on land.
- Runoff is precipitation that flows over the surface of the land. This water may travel to a river, lake, or ocean. Runoff may pick up fertilizer and other pollutants and deliver them to the water body where it ends up. In this way, runoff may pollute bodies of water.
- Infiltration is the process by which water soaks into the ground. Some of the water may seep deep underground. Some may stay in the soil, where plants can absorb it with their roots.
In all these ways, water keeps cycling. The water cycle repeats over and over again. Who knows? Maybe a water molecule that you drink today once quenched the thirst of a dinosaur.
Lesson Summary
- Water is a simple chemical compound. It exists on Earth in all three states of matter: liquid, gas, and solid. As a gas, water is called water vapor. As a solid, water is called ice.
- Oceans of salt water cover much of Earth’s surface. Freshwater is water that contains little or no salt. Most of Earth’s freshwater is frozen in ice caps and glaciers.
- Earth’s water is constantly recycled through the water cycle. Water keeps changing state as it goes through the cycle. The water cycle includes processes such as evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
Lesson Review Questions
Recall
1. What is freshwater?
2. Where is most of Earth’s freshwater found?
3. What process changes water from a liquid to a gas? From a gas to a liquid?
4. Define infiltration and runoff.
Apply Concepts
5. Describe the substance known as water.
6. Why does most precipitation fall into the oceans?
Think Critically
7. Apply lesson concepts to explain how a forest fire might affect the water cycle.
8. Explain why this statement is true: “The water you drink today may once have quenched the thirst of a dinosaur.”
9. How does the Sun drive the water cycle? What would happen to the water cycle if the Sun decreased its intensity by half?
Points to Consider
As water moves through the water cycle, it spends some time on Earth’s surface as freshwater.
- Where is freshwater found on Earth’s surface?
- How do people use freshwater on Earth’s surface?
- Log in or register to post comments
- Email this page